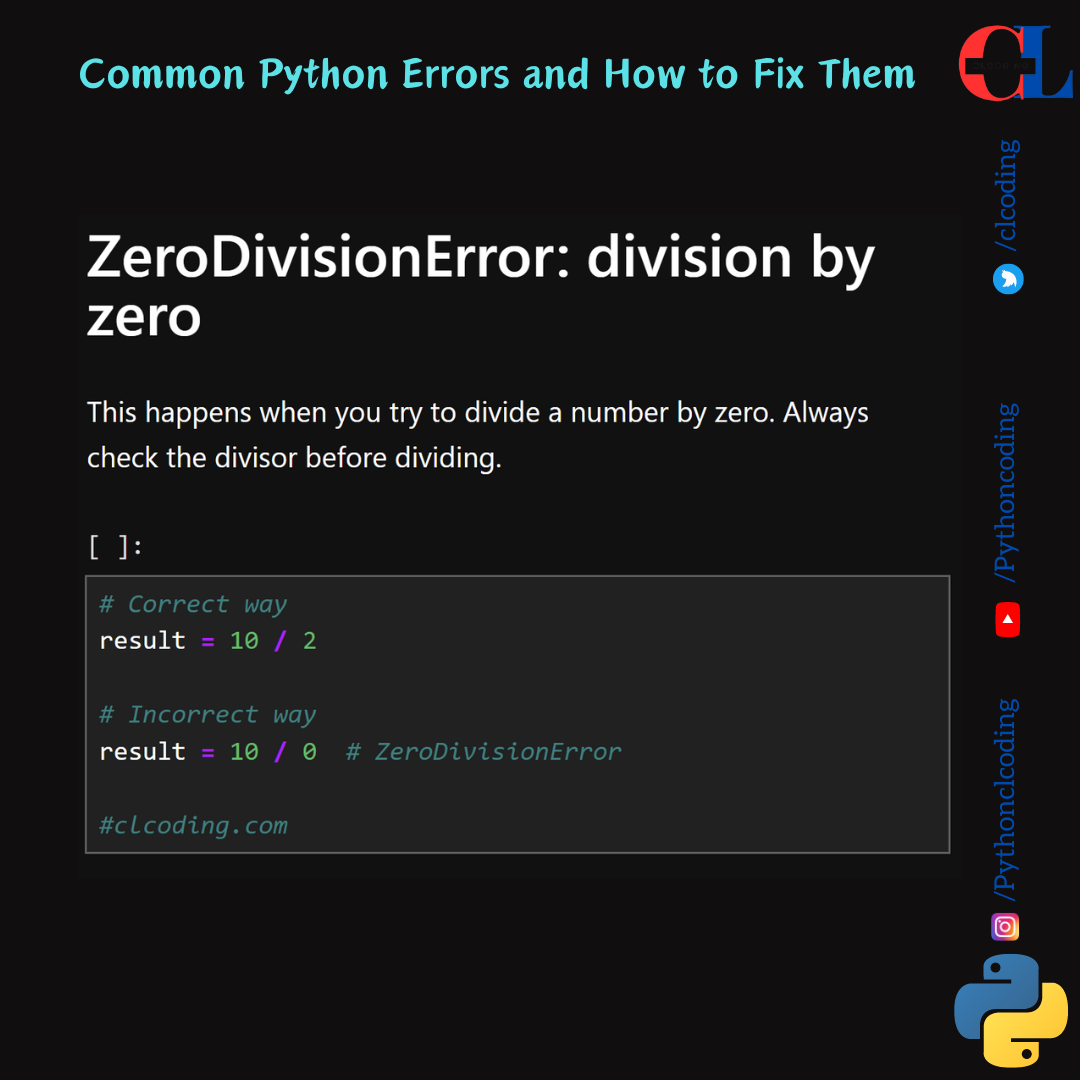
ZeroDivisionError: division by zero
This happens when you try to divide a number by zero. Always check the divisor before dividing.
# Correct way
result = 10 / 2
# Incorrect way
result = 10 / 0 # ZeroDivisionError
#clcoding.com
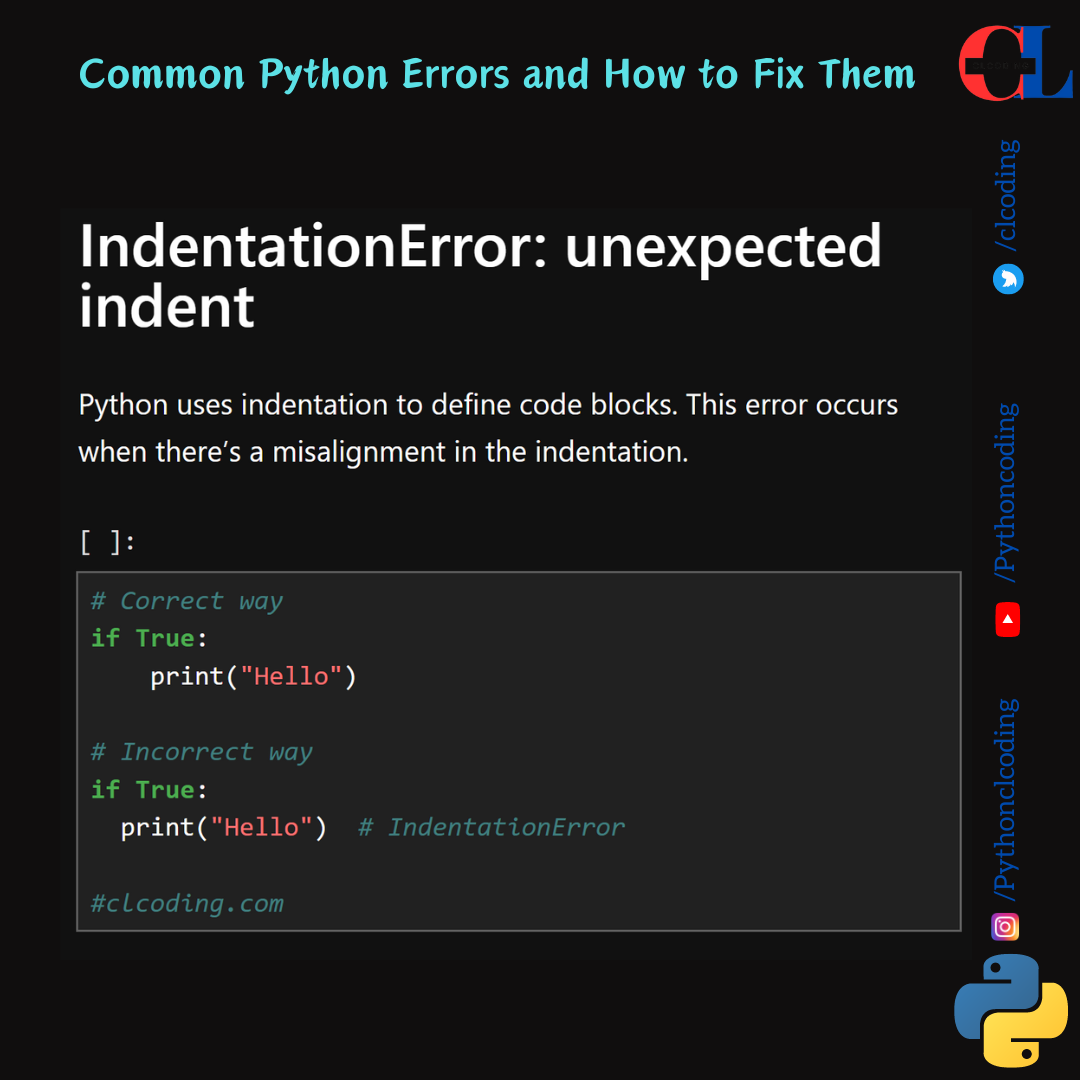
IndentationError: unexpected indent
Python uses indentation to define code blocks. This error occurs when there’s a misalignment in the indentation.
# Correct way
if True:
print("Hello")
# Incorrect way
if True:
print("Hello") # IndentationError
#clcoding.com
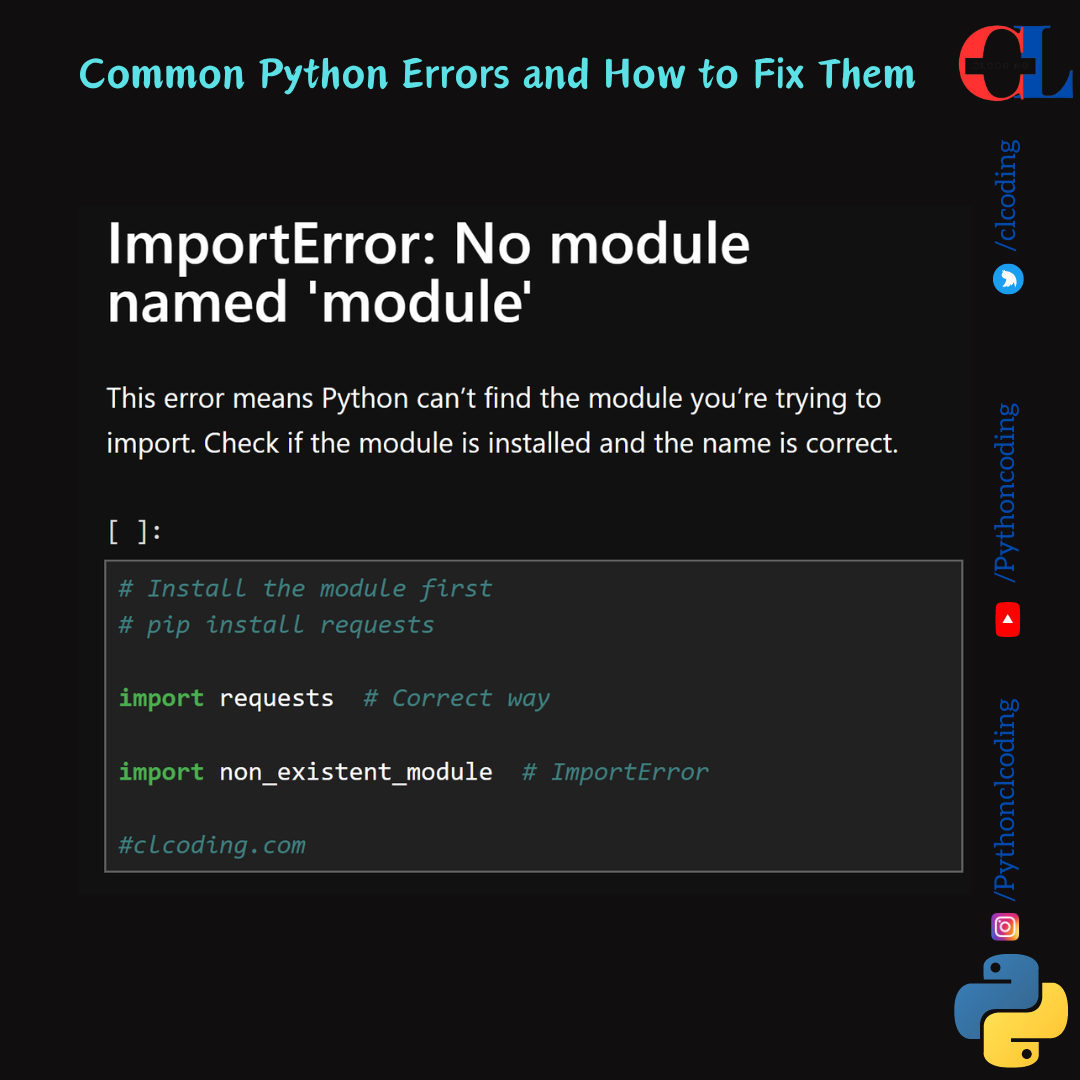
ImportError: No module named 'module'
This error means Python can’t find the module you’re trying to import. Check if the module is installed and the name is correct.
# Install the module first
# pip install requests
import requests # Correct way
import non_existent_module # ImportError
#clcoding.com
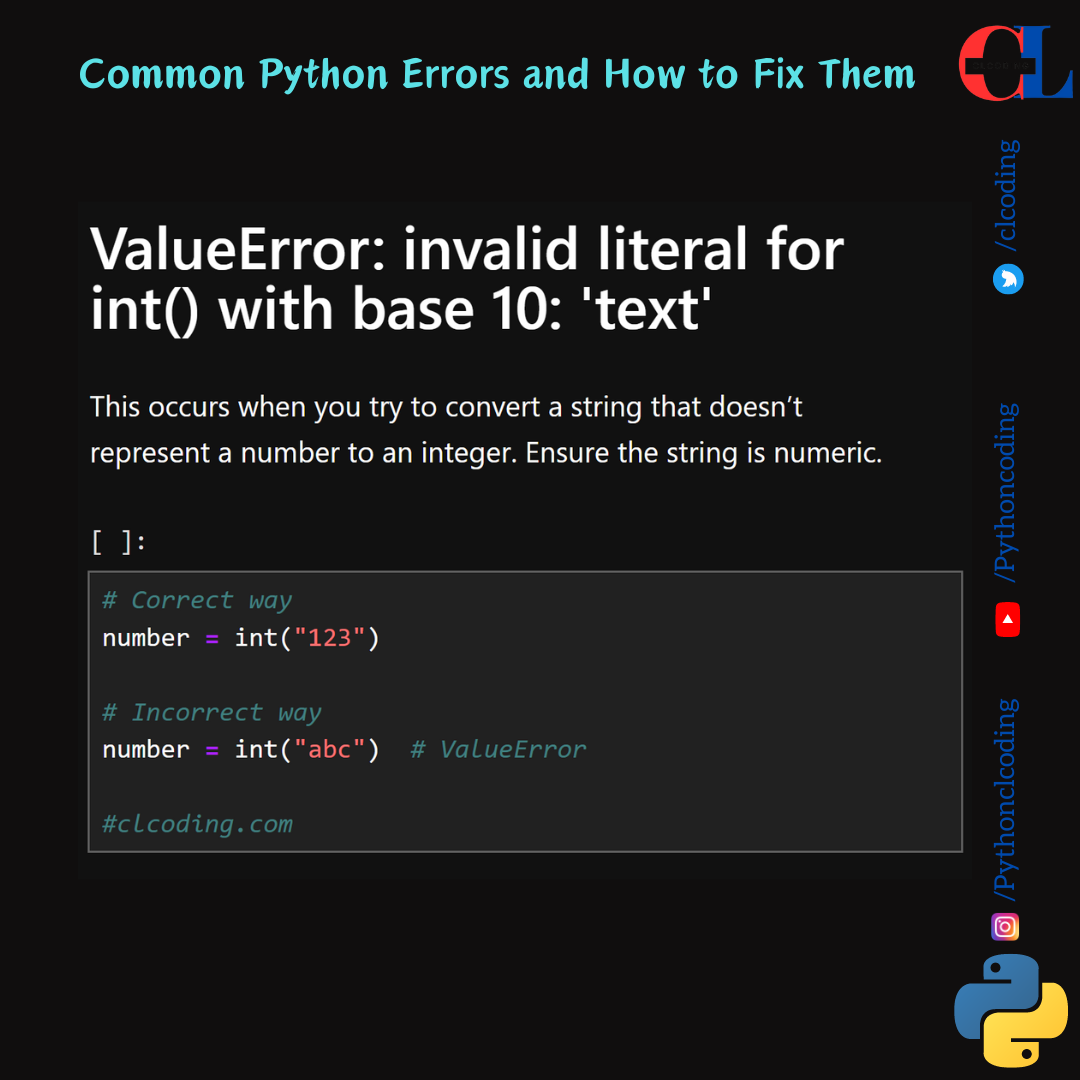
ValueError: invalid literal for int() with base 10: 'text'
This occurs when you try to convert a string that doesn’t represent a number to an integer. Ensure the string is numeric.
# Correct way
number = int("123")
# Incorrect way
number = int("abc") # ValueError
#clcoding.com
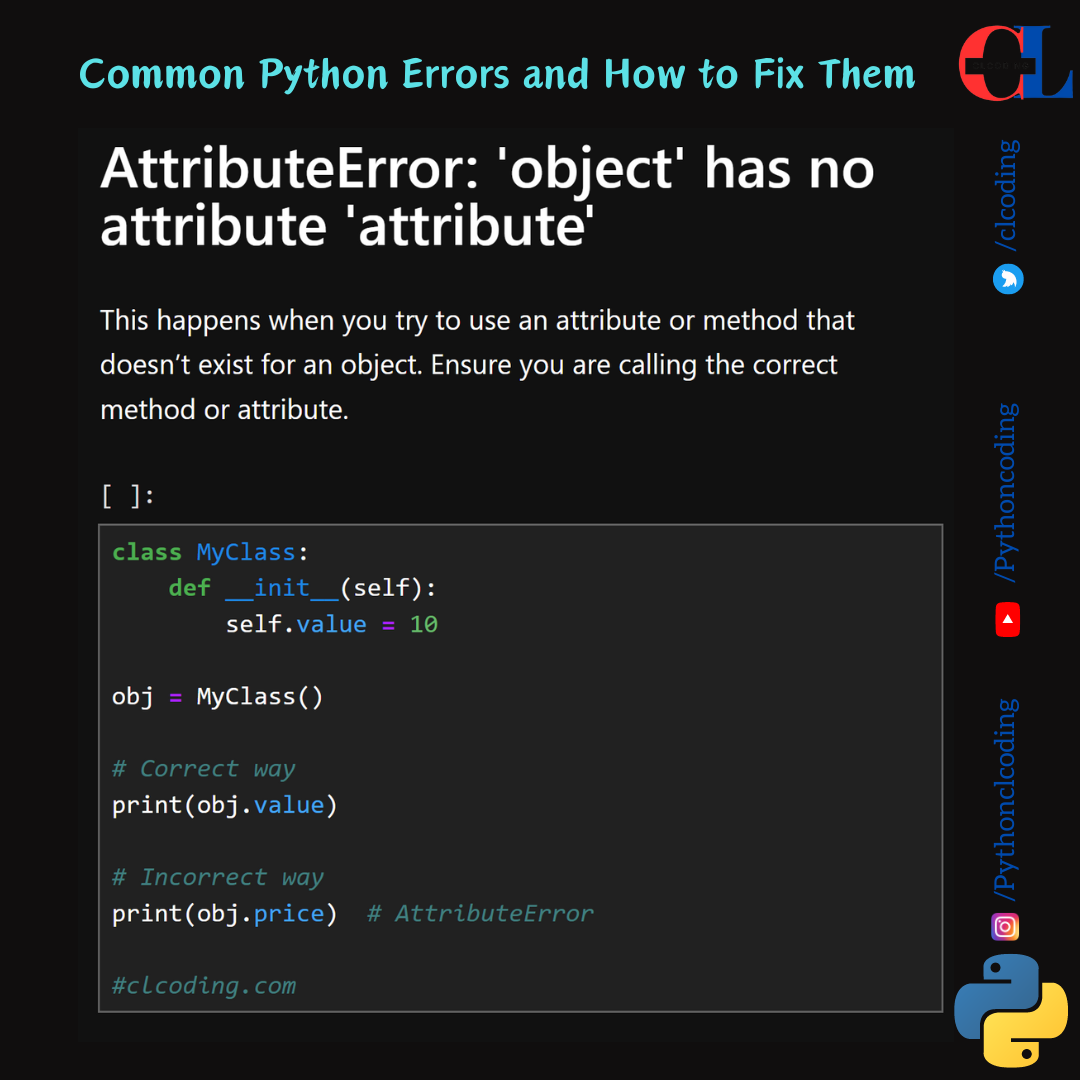
AttributeError: 'object' has no attribute 'attribute'
This happens when you try to use an attribute or method that doesn’t exist for an object. Ensure you are calling the correct method or attribute.
class MyClass:
def __init__(self):
self.value = 10
obj = MyClass()
# Correct way
print(obj.value)
# Incorrect way
print(obj.price) # AttributeError
#clcoding.com
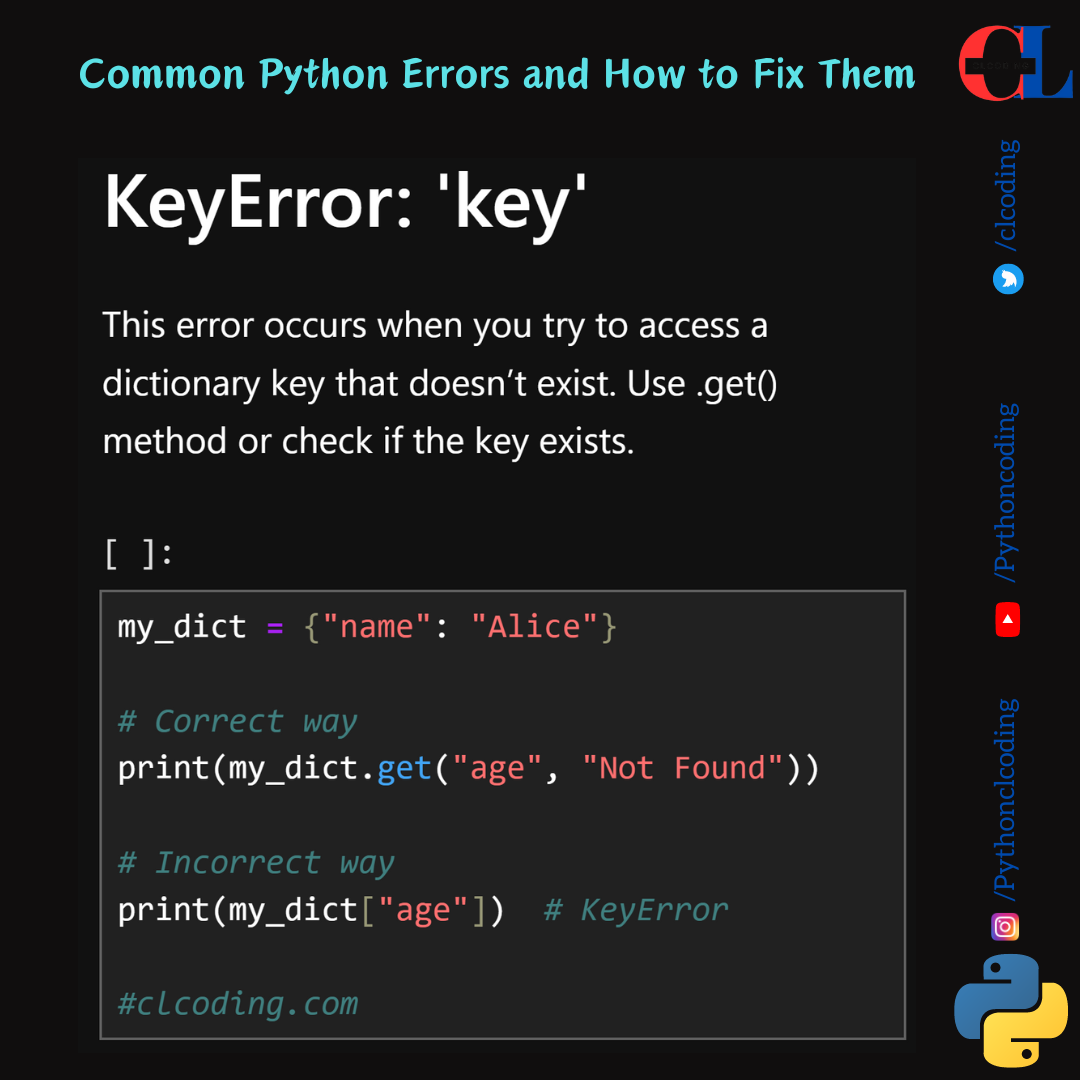
KeyError: 'key'
This error occurs when you try to access a dictionary key that doesn’t exist. Use .get() method or check if the key exists.
my_dict = {"name": "Alice"}
# Correct way
print(my_dict.get("age", "Not Found"))
# Incorrect way
print(my_dict["age"]) # KeyError
#clcoding.com
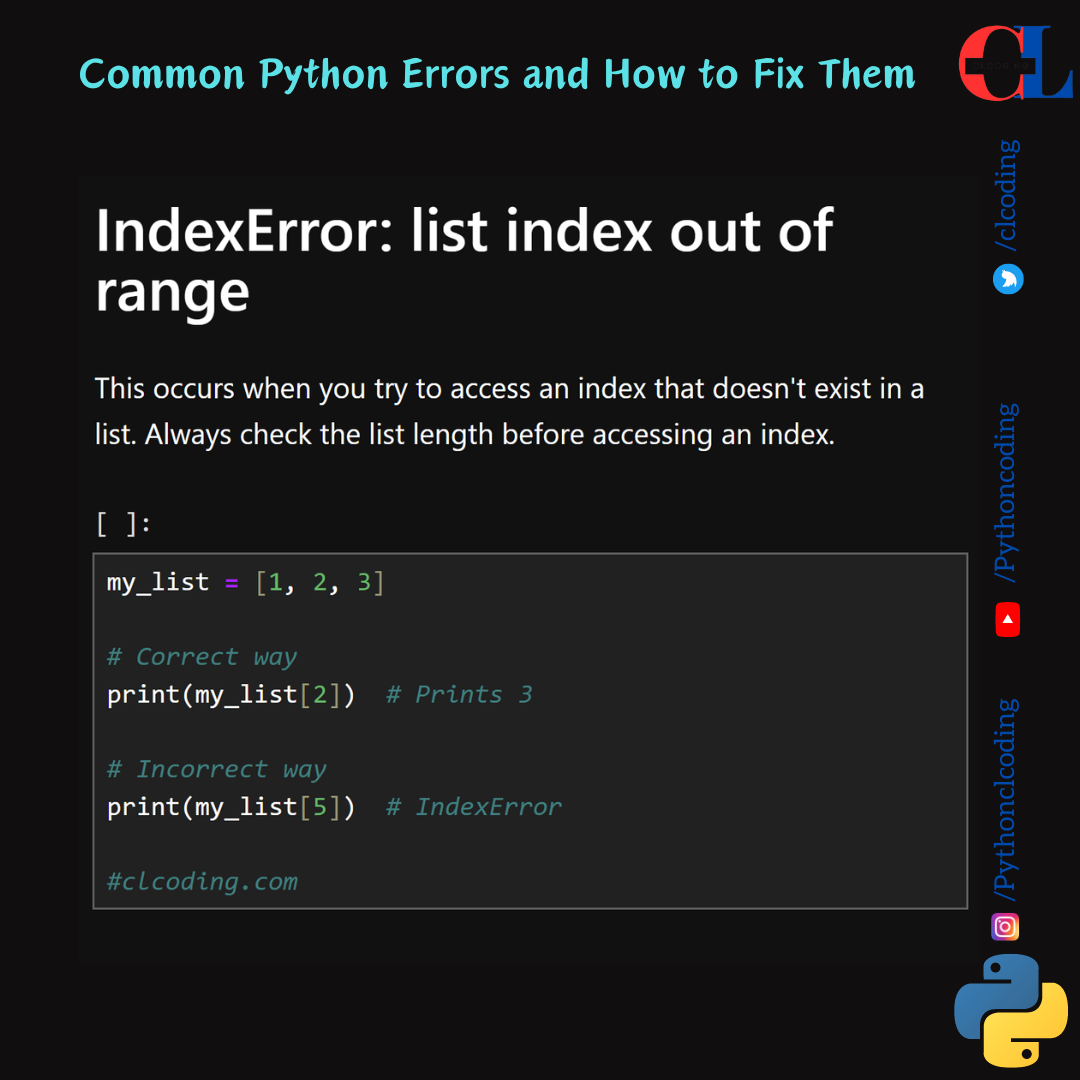
IndexError: list index out of range
This occurs when you try to access an index that doesn't exist in a list. Always check the list length before accessing an index.
my_list = [1, 2, 3]
# Correct way
print(my_list[2]) # Prints 3
# Incorrect way
print(my_list[5]) # IndexError
#clcoding.com
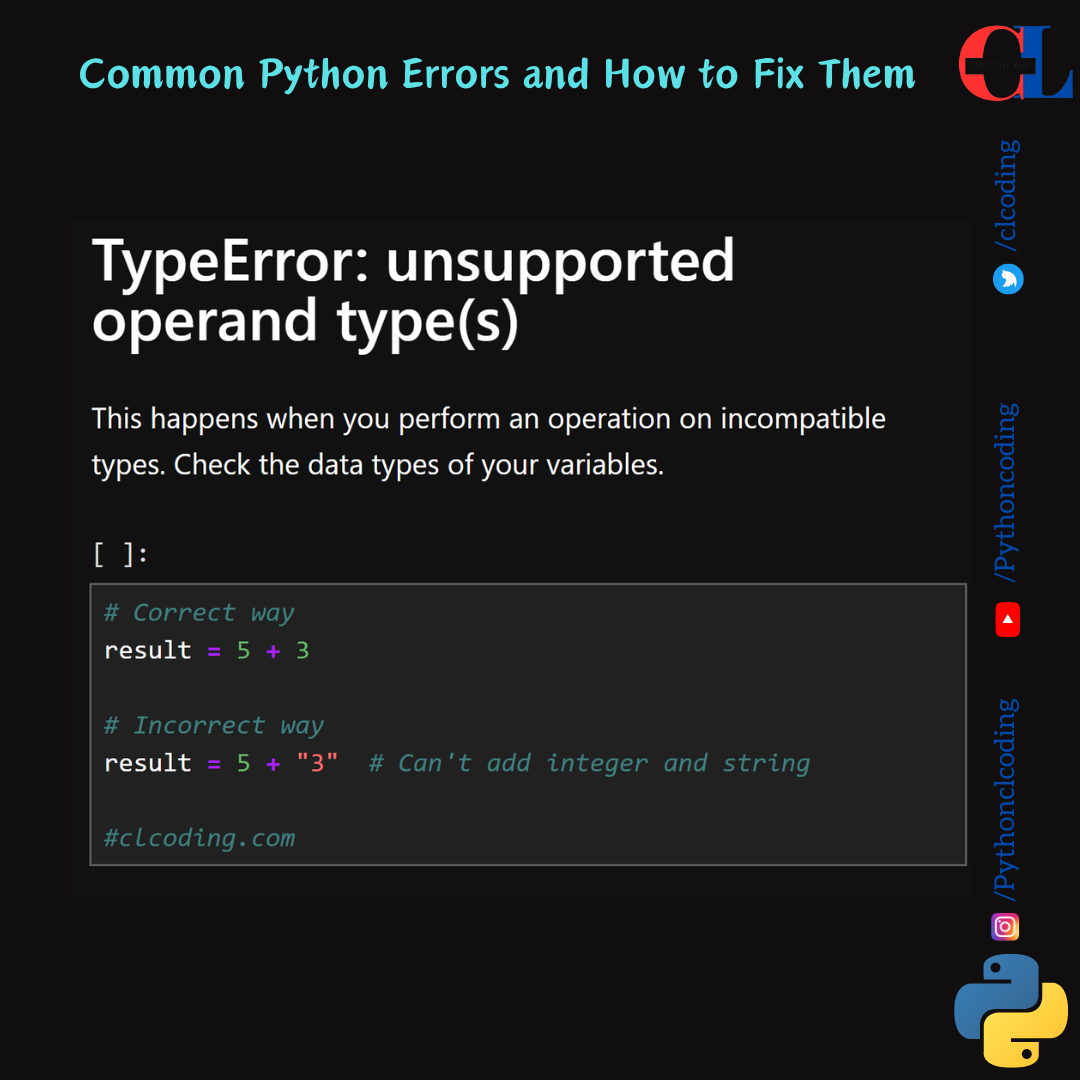
TypeError: unsupported operand type(s)
This happens when you perform an operation on incompatible types. Check the data types of your variables.
# Correct way
result = 5 + 3
# Incorrect way
result = 5 + "3" # Can't add integer and string
#clcoding.com
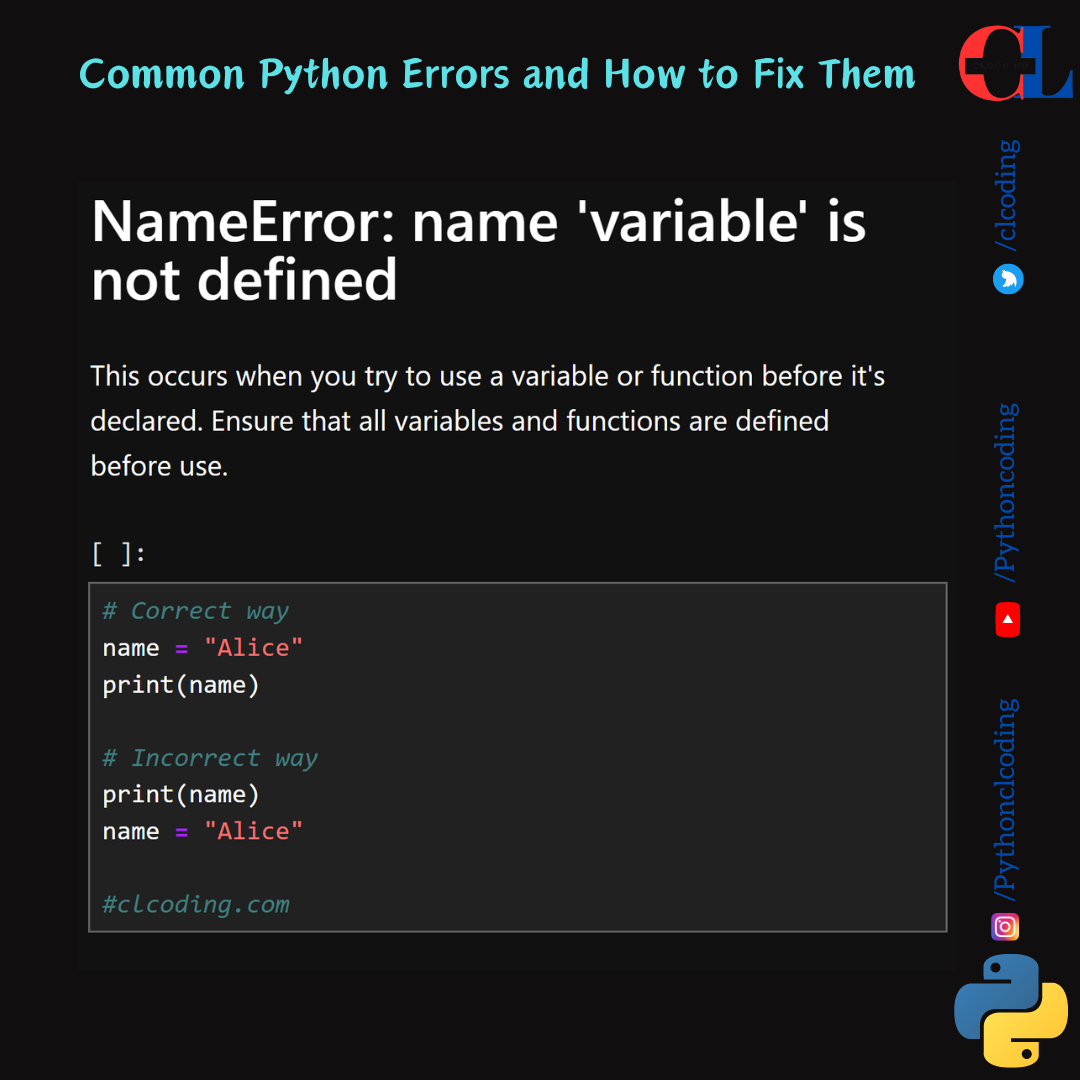
NameError: name 'variable' is not defined
This occurs when you try to use a variable or function before it's declared. Ensure that all variables and functions are defined before use.
# Correct way
name = "Alice"
print(name)
# Incorrect way
print(name)
name = "Alice"
#clcoding.com
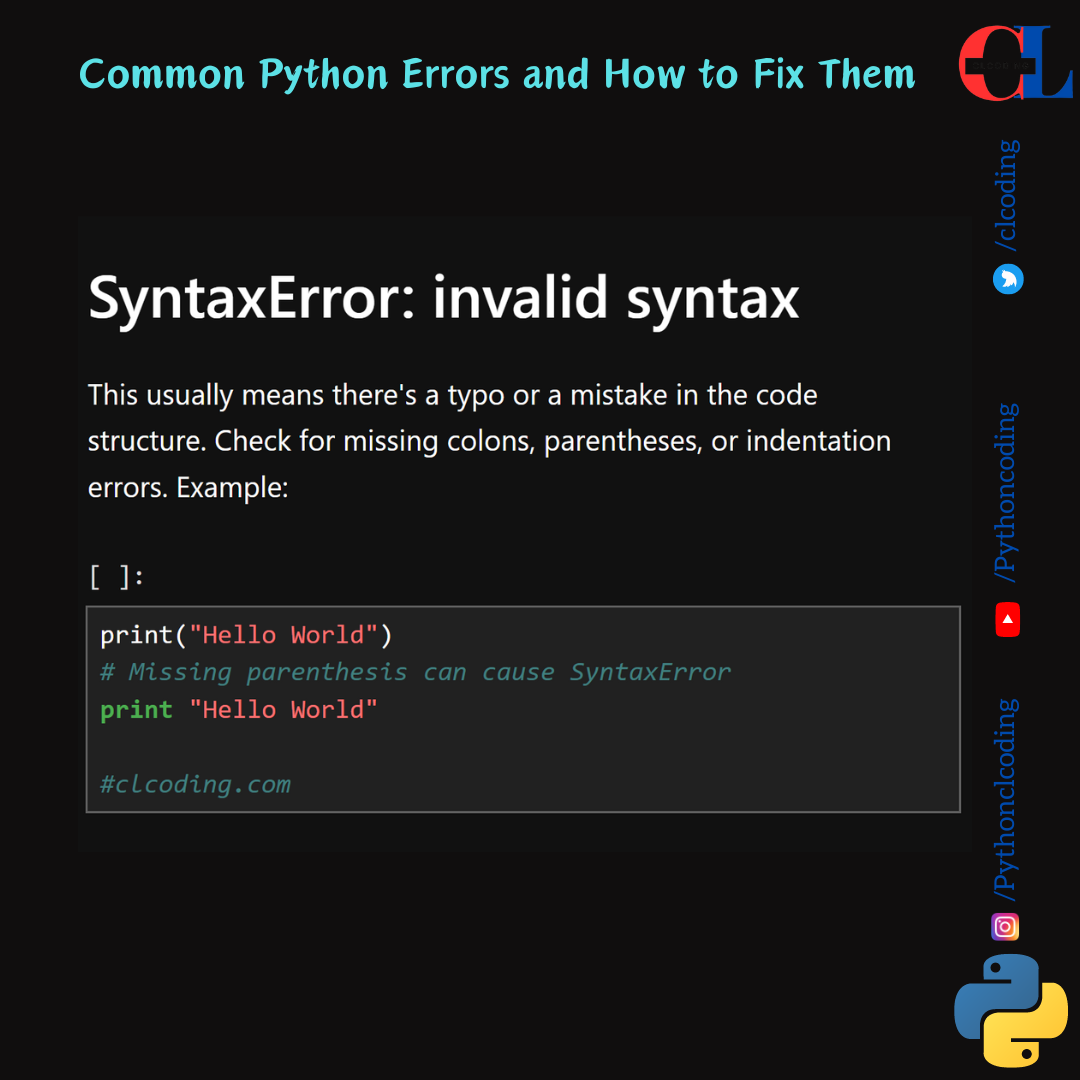
SyntaxError: invalid syntax
This usually means there's a typo or a mistake in the code structure. Check for missing colons, parentheses, or indentation errors. Example:
print("Hello World")
# Missing parenthesis can cause SyntaxError
print "Hello World"
#clcoding.com









.png)







.png)
























0 Comments:
Post a Comment