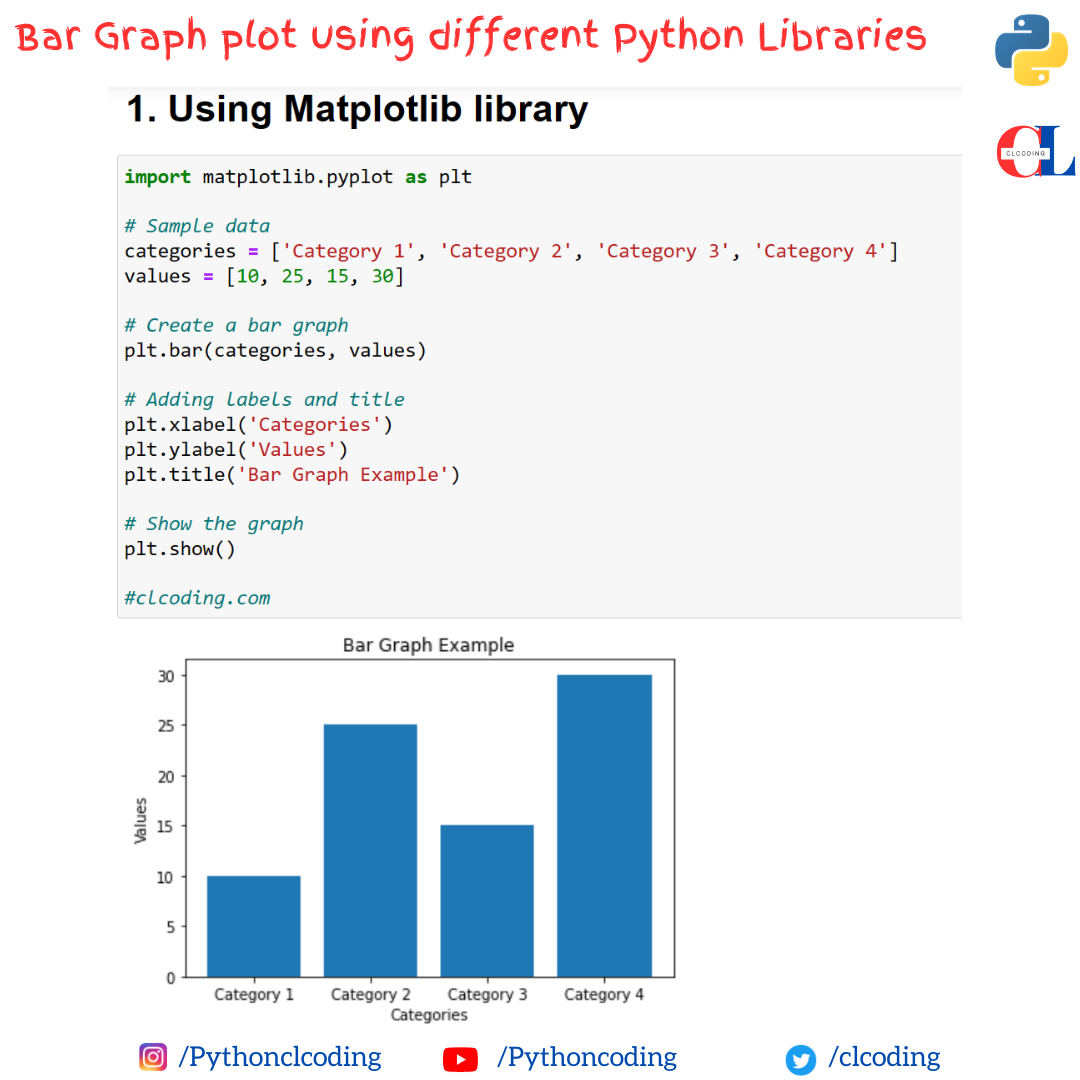
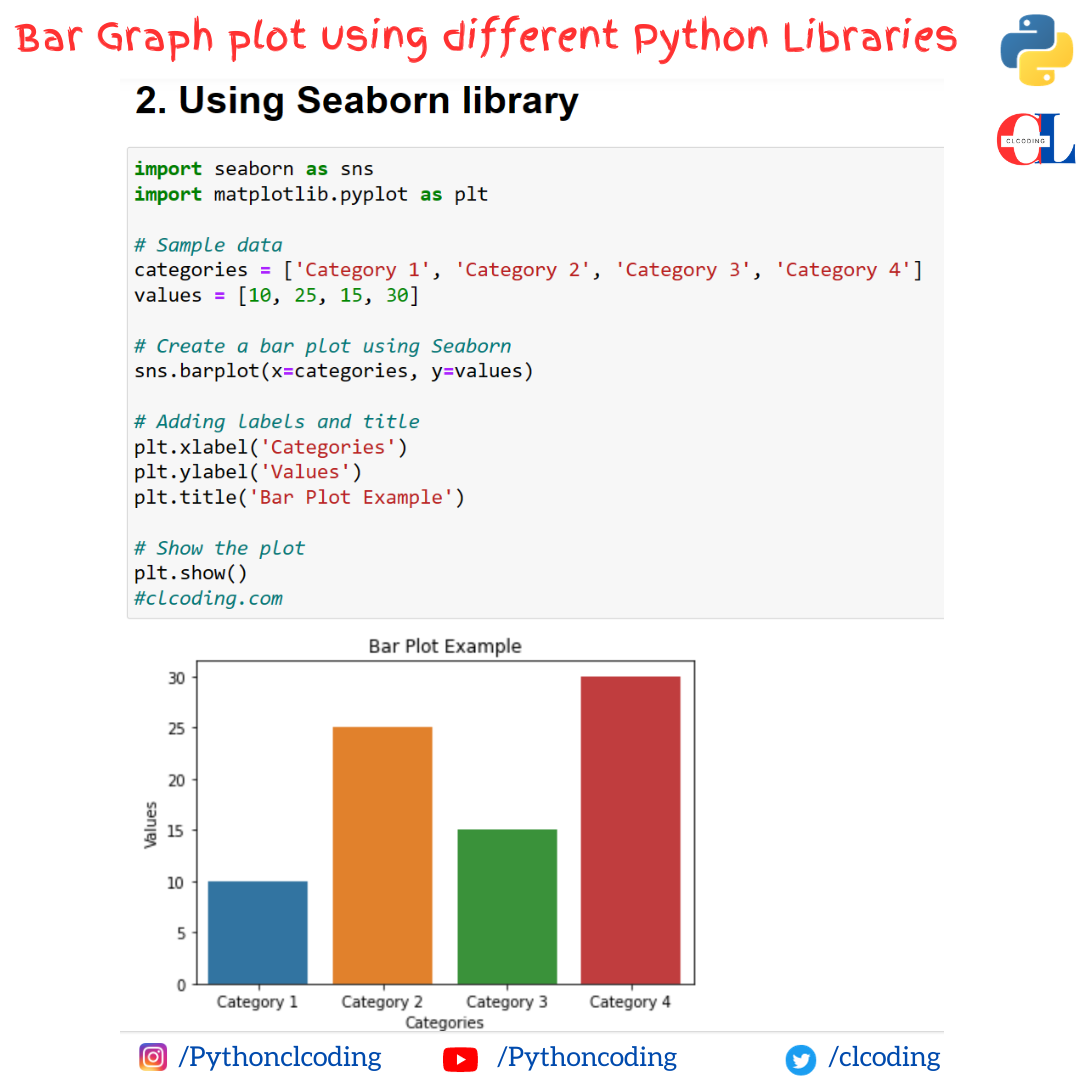
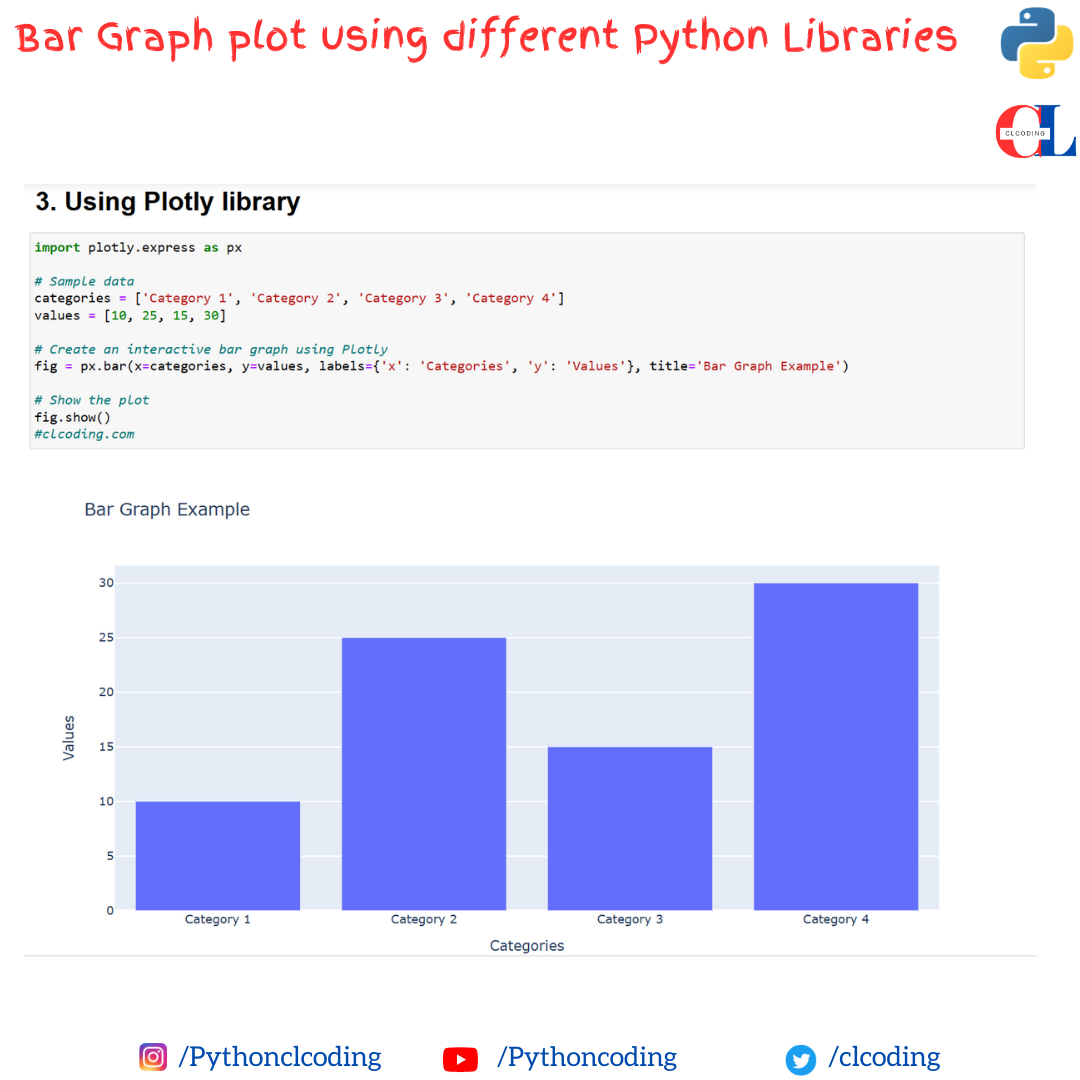
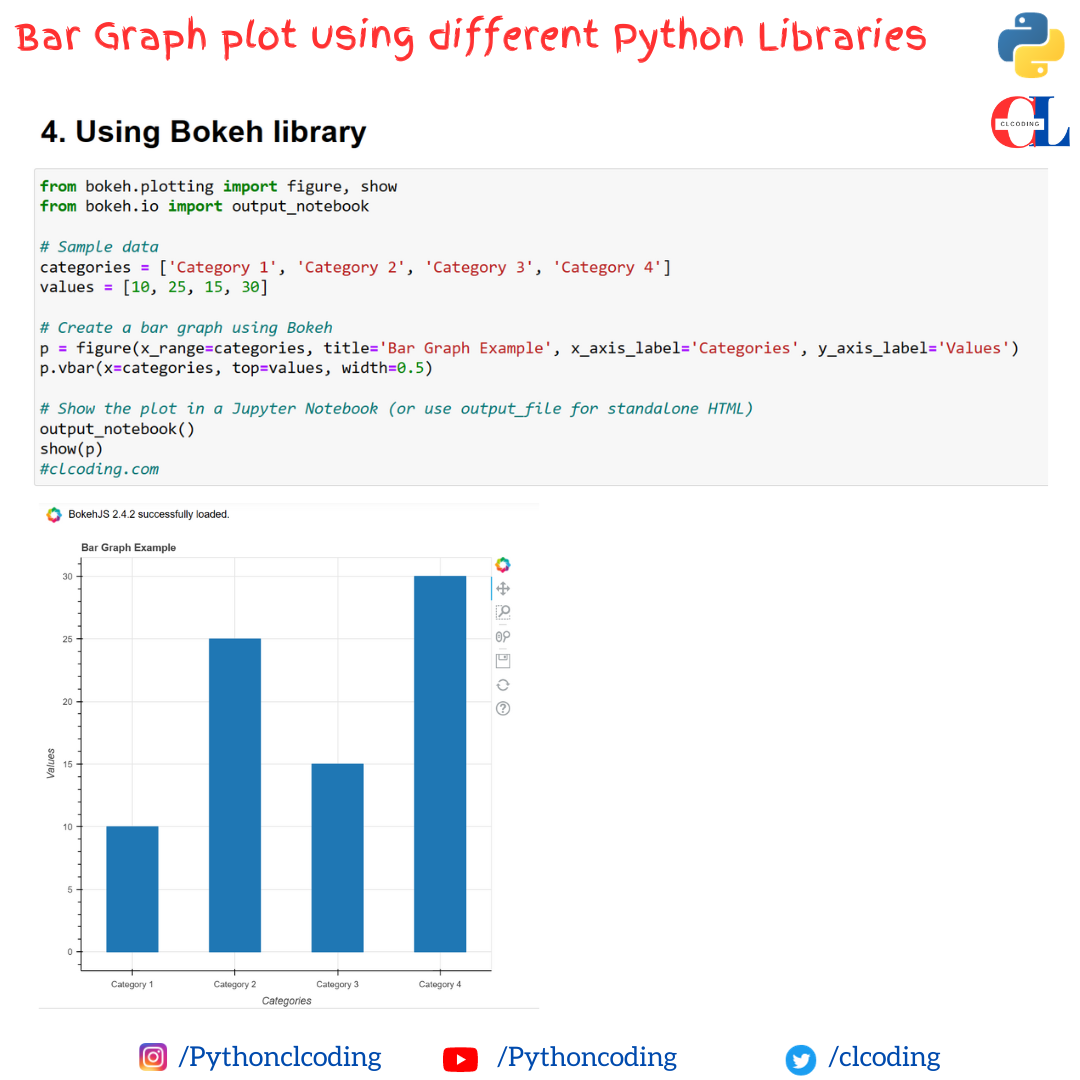
Python Coding January 13, 2024 Python No comments




Python Coding January 13, 2024 Books No comments
Python Coding January 13, 2024 Python Coding Challenge No comments
Python Coding January 13, 2024 Python No comments
Level 1: Basic Function
Level 2: Function with Parameters
Level 3: Return Values
Level 4: Default Parameters
Level 5: Docstrings
Level 6: Variable Scope
Level 7: Recursion
Level 8: Lambda Functions
Level 9: Function Decorators
Level 10: Advanced Functions
Python Coding January 12, 2024 Python Coding Challenge No comments
1. Which value is used to represent the first index of
list?
(a) 1 (b) 0
(c) −1 (d) a
Ans. (b) To access the list’s elements, index number is used. The
index number should be an integer. Index of 0 refers to first
element, 1 refers to second element and so on.
2. Choose the output of following Python code.
1= list ()
print ( 1)
(a) [] (b) ()
(c) [,] (d) Empty
Ans. (a) Empty list can be created in Python using []. To create
empty list, list () is also used.
3. Suppose list
1= [10, 20, 30, 40, 50, 60, 70]
print( 1[−3])
(a) 30 (b) 50
(c) 40 (d) Error
Ans. (b) The index of −1 refers to the last element, −2 refers to the
second last element and so on. Hence, −3 refers to third last
element, i.e. 50.
4. Choose the output from following code.
list1 = [‘A’, ‘R’, ‘I’,‘H’,‘A’,‘N’,‘T’]
print (list1 [7])
(a) T (b) N
(c) A (d) Error
Ans. (d) In the given code, we are trying to access 8th element
from the list which does not exist as we are having total 7
elements for which the last index is 6. So, Python will give
an IndexError.
5. Which function is used to insert an element at
specified position in the list?
(a) extend () (b) append ()
(c) insert () (d) add ()
Ans. (c) insert () function is used to insert an element at specified
position in the list. This method takes two arguments : one
for index number and second for element value.
Syntax list_name.insert(index, element)
6. Choose the correct option for the following.
l1 = [2, 5, 7]
l = l1+ 5
print (l)
(a) [7, 10, 12]
(b) [2, 5, 7, 5]
(c) [5, 2, 5, 7]
(d) TypeError
Ans. (d) + operator cannot add list with other type as number or
string because this operator is used only with list types.
So, it will give TypeError as it can only concatenate list (not
“int”) to list.
7. What is the output of following code?
l1 = [3, 2, 6]
l = l1 * 2
print (l)
(a) [3, 2, 6, 3, 2, 6]
(b) [6, 4, 12]
(c) [3, 4, 12]
(d) TypeError
Ans. (a) * operator can repeat the elements of the list.
Syntax list = list1 * digit
8. Which of the following is true regarding lists in
Python?
(a) Lists are immutable.
(b) Size of the lists must be specified before its initialisation.
(c) Elements of lists are stored in contiguous memory
location.
(d) size(list1) command is used to find the size of lists.
Ans. (c) Elements of lists are stored in contiguous memory
location, so it is true regarding lists in Python.
9. Suppose list1 is [56, 89, 75, 65, 99], what is the
output of list1 [− 2]?
(a) Error (b) 75
(c) 99 (d) 65
Ans. (d) −1 corresponds to the last index in the list, −2 represents
the second last element and so on.
So, the output for list1 [− 2] is 65 because 65 is second last
element of list1.
10. Identify the output of following code.
List1=[1, 2, 3, 7, 9]
L=List1.pop(9)
print(L)
(a) Syntax error (b) 9
(c) [1, 2, 3, 7] (d) None of these
Ans. (a) In pop(9), parentheses put index number instead of
element. In the given list, maximum index number is 4, then
9 is out of index range.
11. Suppose list1 is [2445,133,12454,123], what is the
output of max(list1)?
(a) 2445 (b) 133
(c) 12454 (d)123
Ans. (c) max() returns the maximum element in the list. From
given options, 12454 is the element with maximum value.
12. To add a new element to a list, which command will
we use?
(a) list1.add(8)
(b) list1.append(8)
(c) list1.addLast(8)
(d) list1.addEnd(8)
Ans. (b) We use the function append() to add an element to the list.
13. What will be the output of the following Python
code?
list1=[9, 5, 3, 5, 4]
list1[1:2]=[7,8]
print(list1)
(a) [9,5, 3, 7, 8] (b) [9, 7, 8, 3, 5, 4]
(c) [9,[ 7, 8], 3, 5,4] (d) Error
Ans. (b) In the piece of code, slice assignment has been
implemented. The sliced list is replaced by the assigned
elements in the list.
14. Consider the declaration a=[2, 3, ‘Hello’, 23.0].
Which of the following represents the data type of
‘a’?
(a) String (b) Tuple
(c) Dictionary (d) List
Ans. (d) List contains a sequence of heterogeneous elements
which store integer, string as well as object. It can created to
put elements separated by comma (,) in square brackets [].
15. Identify the output of the following Python
statement.
x=[[1, 2, 3, 4], [5, 6, 7, 8]]
y=x [0] [2]
print(y)
(a) 3 (b) 4
(c) 6 (d) 7
Ans. (a) x is a list, which has two sub-lists in it. Elements of first
list will be represented by [0] [i] and elements of second list
will be represented by [1] [i].
16. Which method will empty the entire list?
(a) pop() (b) clear()
(c) sort() (d) remove()
Ans. (b) clear() method is used to remove all the items of a list.
This method will empty the entire list.
Syntax
list_name.clear()
17. Which of the following allows us to sort the list
elements in descending order?
(a) reverse = True
(b) reverse = False
(c) sort (descending)
(d) sort. descending
Ans. (a) sort() is used to sort the given list in ascending order. The
sort() has an argument called reverse = True. This allows us
to sort the list elements in descending order.
18. Identify the correct output.
>>>l1 = [34, 65, 23, 98]
>>>l1. insert(2, 55)
>>>l1
(a) [34, 65, 23, 55] (b) [34, 55, 65, 23, 98]
(c) [34, 65, 55, 98] (d) [34, 65, 55, 23, 98]
Ans. (d) insert() is used to insert an element at specified position
in the list. This method takes two arguments : one for index
number and second for element value.
Syntax
list_name.insert(index, element)
19. Find the output from the following code.
list1=[2, 5, 4, 7, 7, 7, 8, 90]
del list1[2 : 4]
print(list1)
(a) [2, 5, 7, 7, 8, 90] (b) [5, 7, 7, 7, 8, 90]
(c) [2, 5, 4, 8, 90] (d) Error
Ans. (a) del keyword is used to delete the elements from the list.
20. Slice operation is performed on lists with the use of
(a) semicolon (b) comma
(c) colon (d) hash
Ans. (c) In Python list, there are multiple ways to print the whole
list with all the elements, but to print a specific range of
elements from the list, we use slice operation. Slice
operation is performed on lists with the use of colon (:).
Python Coding January 12, 2024 Python No comments
Python Coding January 12, 2024 Python Coding Challenge No comments
What is the output of following Python code?
a =[[0, 1, 2], [3, 4, 5, 6]]
b =a[1] [2]
print (b)
Let's break down your code step by step:
a = [[0, 1, 2], [3, 4, 5, 6]]
Here, you have defined a list a that contains two sub-lists. The first sub-list is [0, 1, 2], and the second sub-list is [3, 4, 5, 6]. So, a is a list of lists.
b = a[1][2]
This line of code is accessing elements in the nested list. Let's break it down:
a[1] accesses the second sub-list in a. In Python, indexing starts from 0, so a[1] refers to [3, 4, 5, 6].
[2] then accesses the third element in this sub-list. Again, indexing starts from 0, so a[1][2] refers to the element at index 2 in the sub-list [3, 4, 5, 6].
As a result, b is assigned the value 5, which is the third element in the second sub-list.
print(b)
Finally, the print(b) statement outputs the value of b, which is 5, to the console.
So, when you run this code, the output will be:
5
This is because b contains the value at index [1][2] in the nested list a, which is 5.
Python Coding January 12, 2024 Python Coding Challenge No comments
def fun(num):
if num > 10:
return num - 10
return fun(fun(num + 11))
print(fun(5))
Python Coding January 11, 2024 Python Coding Challenge No comments
return (a, b, c)
return a + b + c
return a, b, c
All three of the provided return statements are valid in Python, but they have different implications:
return (a, b, c): This returns a single tuple containing the values of a, b, and c. For example, if a = 1, b = 2, and c = 3, the function would return the tuple (1, 2, 3).
return a + b + c: This returns the sum of a, b, and c. If a = 1, b = 2, and c = 3, the function would return the value 6.
return a, b, c: This returns a tuple containing the values of a, b, and c. This is a more concise way of expressing the first option. For the same example values, it would return the tuple (1, 2, 3).
Choose the one that fits your specific use case and the desired return value format in your function.
Python Coding January 11, 2024 Python Coding Challenge No comments
The code you provided is attempting to generate a Fibonacci sequence and append the values to the list lst. However, it seems like there's a small mistake in your code. The range in the list comprehension should go up to 4, not 5, to generate the Fibonacci sequence up to the 4th element. Here's the corrected code:
lst = [0, 1]
[lst.append(lst[k - 1] + lst[k - 2]) for k in range(2, 5)]
print(lst)
After running this code, lst will be:
[0, 1, 1, 2, 3]
This list represents the Fibonacci sequence up to the 4th element. The initial list [0, 1] is extended by three more elements generated by adding the last two elements of the list to get the next one.
Python Coding January 11, 2024 Python Coding Challenge No comments
You can use list comprehension to generate a list of integer coordinates for all points in the first quadrant from (1, 1) to (5, 5). Here's an example in Python:
print(coordinates)
This code will produce a list of tuples where each tuple represents a coordinate in the first quadrant, ranging from (1, 1) to (5, 5). The range(1, 6) is used to include values from 1 to 5 (inclusive) for both x and y.
After running this code, coordinates will contain the following list:
[(1, 1), (1, 2), (1, 3), (1, 4), (1, 5), (2, 1), (2, 2), (2, 3), (2, 4), (2, 5), (3, 1), (3, 2), (3, 3), (3, 4), (3, 5), (4, 1), (4, 2), (4, 3), (4, 4), (4, 5), (5, 1), (5, 2), (5, 3), (5, 4), (5, 5)]
Python Coding January 10, 2024 Python Coding Challenge No comments
x = 15
y = 10
result = x if x < y else y
print(result)
Python Coding January 09, 2024 Books No comments
Delve into the realm of generative AI and large language models (LLMs) while exploring modern deep learning techniques, including LSTMs, GRUs, RNNs with new chapters included in this 50% new edition overhaul
Purchase of the print or Kindle book includes a free eBook in PDF format.
The ability to use algorithms to solve real-world problems is a must-have skill for any developer or programmer. This book will help you not only to develop the skills to select and use an algorithm to tackle problems in the real world but also to understand how it works.
You'll start with an introduction to algorithms and discover various algorithm design techniques, before exploring how to implement different types of algorithms, with the help of practical examples. As you advance, you'll learn about linear programming, page ranking, and graphs, and will then work with machine learning algorithms to understand the math and logic behind them.
Case studies will show you how to apply these algorithms optimally before you focus on deep learning algorithms and learn about different types of deep learning models along with their practical use.
You will also learn about modern sequential models and their variants, algorithms, methodologies, and architectures that are used to implement Large Language Models (LLMs) such as ChatGPT.
Finally, you'll become well versed in techniques that enable parallel processing, giving you the ability to use these algorithms for compute-intensive tasks.
By the end of this programming book, you'll have become adept at solving real-world computational problems by using a wide range of algorithms.
This computer science book is for programmers or developers who want to understand the use of algorithms for problem-solving and writing efficient code.
Whether you are a beginner looking to learn the most used algorithms concisely or an experienced programmer looking to explore cutting-edge algorithms in data science, machine learning, and cryptography, you'll find this book useful.
Python programming experience is a must, knowledge of data science will be helpful but not necessary.
Python Coding January 09, 2024 Python Coding Challenge No comments
a. A function can belong to a module and the module can belong to a
package.
Answer
True
b. A package can contain one or more modules in it.
Answer
True
c. Nested packages are allowed.
Answer
True
d. Contents of sys.path variable cannot be modified.
Answer
False
e. In the statement import a.b.c, c cannot be a function.
Answer
True
f. It is a good idea to use * to import all the functions/classes defined in a
module.
Answer
True
Python Coding January 09, 2024 Coursera, SQL No comments
How to use the PostgreSQL database effectively
Explore database design principles
Dive into database architecture and deployment strategies
Compare and contrast SQL and NoSQL database design approaches and acquire skills applicable to data mining and application development
Python Coding January 09, 2024 Coursera, Data Strucures, Python No comments
Explain the principles of data structures & how they are used
Create programs that are able to read and write data from files
Store data as key/value pairs using Python dictionaries
Accomplish multi-step tasks like sorting or looping using tuples
Python Coding January 09, 2024 Coursera, web application No comments
Installing your development environment
Developing a database application with PHP and MySQL
Using JavaScript to interact with a PHP web app
Modeling many-to-many relationships
Python Coding January 09, 2024 AI, Coursera No comments
Learn how generative AI works
Explore the benefits and drawbacks of generative AI
Learn how generative AI can integrate into our daily lives
Python Coding January 09, 2024 Coursera, Python No comments
Learn Python 3 basics, from the basics to more advanced concepts like lists and functions.
Practice and become skilled at solving problems and fixing errors in your code.
Gain the ability to write programs that fetch data from internet APIs and extract useful information.
Python Coding January 08, 2024 Python Coding Challenge No comments
complex_num = 4 + 3j
print(abs(complex_num))
The above code calculates the absolute value (magnitude) of a complex number and prints the result. In this case, the complex number is 4 + 3j. The absolute value of a complex number is given by the square root of the sum of the squares of its real and imaginary parts.
Let's break it down:
complex_num = 4 + 3j
This line creates a complex number with a real part of 4 and an imaginary part of 3.
print(abs(complex_num))
This line calculates the absolute value of the complex number using the abs function and then prints the result. The output will be:
5.0
So, the absolute value of the complex number 4 + 3j is 5.0.
Python Coding January 08, 2024 Coursera, Data Science No comments
Conduct an inferential statistical analysis
Discern whether a data visualization is good or bad
Enhance a data analysis with applied machine learning
Analyze the connectivity of a social network
Python Coding January 08, 2024 AI, Coursera, Data Science No comments
What is AI and AI use cases, Machine Learning, Deep Leaning, and how training and inference happen in a Deep Learning Workflow.
The history and architecture of GPUs, how they differ from CPUs, and how they are revolutionizing AI.
Become familiar with deep learning frameworks, AI software stack, and considerations when deploying AI workloads on a data center on prem or cloud.
Requirements for multi-system AI clusters and considerations for infrustructure planning, including servers, networking, storage and tools.
Python Coding January 08, 2024 Coursera, IBM, Software No comments
Develop a DevOps mindset, practice Agile philosophy & Scrum methodology - essential to succeed in the era of Cloud Native Software Engineering
Create applications using Python language, using various programming constructs and logic, including functions, REST APIs, and libraries
Build applications composed of microservices and deploy using containers (e.g. Docker, Kubernetes, and OpenShift) & serverless technologies
Employ tools for automation, continuous integration (CI) and continuous deployment (CD) including Chef, Puppet, GitHub Actions, Tekton and Travis.
Python Coding January 08, 2024 AI, Coursera No comments
Learn about the business problems that AI/ML can solve as well as the specific AI/ML technologies that can solve them.
Learn important tasks that make up the workflow, including data analysis and model training and about how machine learning tasks can be automated.
Use ML algorithms to solve the two most common supervised problems regression and classification, and a common unsupervised problem: clustering.
Explore advanced algorithms used in both machine learning and deep learning. Build multiple models to solve business problems within a workflow.
Python Coding January 08, 2024 AI, Coursera No comments
Compare AI with human intelligence, broadly understand how it has evolved since the 1950s, and identify industry applications
Identify and use creative and critical thinking, design thinking, data fluency, and computational thinking as they relate to AI applications
Explain how the development and use of AI requires ethical considerations focusing on fairness, transparency, privacy protection and compliance
Describe how thinking skills embedded in Australian curricula can be used to solve problems where AI has the potential to be part of the solution
Python Coding January 07, 2024 Course, Coursera, MICHIGAN No comments
Add interacitivity to web pages with Javascript
Describe the basics of Cascading Style Sheets (CSS3)
Use the Document Object Model (DOM) to modify pages
Apply responsive design to enable page to be viewed by various devices
This Specialization covers the basics of how web pages are created – from writing syntactically correct HTML and CSS to adding JavaScript to create an interactive experience. While building your skills in these topics you will create websites that work seamlessly on mobile, tablet, and large screen browsers. During the capstone you will develop a professional-quality web portfolio demonstrating your growth as a web developer and your knowledge of accessible web design. This will include your ability to design and implement a responsive site that utilizes tools to create a site that is accessible to a wide audience, including those with visual, audial, physical, and cognitive impairments.
Python Coding January 07, 2024 Python No comments
Lists and sets in Python are both used for storing collections of elements, but they have several differences based on their characteristics and use cases. Here are some key differences between lists and sets in Python:
Ordering:
Lists: Maintain the order of elements. The order in which elements are added is preserved, and you can access elements by their index.
Sets: Do not maintain any specific order. The elements are unordered, and you cannot access them by index.
Uniqueness:
Lists: Allow duplicate elements. You can have the same value multiple times in a list.
Sets: Enforce uniqueness. Each element in a set must be unique; duplicates are automatically removed.
Declaration:
Lists: Created using square brackets [].
Sets: Created using curly braces {} or the set() constructor.
Mutability:
Lists: Mutable, meaning you can change the elements after the list is created. You can add, remove, or modify elements.
Sets: Mutable, but individual elements cannot be modified once the set is created. You can add and remove elements, but you can't change them.
Indexing:
Lists: Allow indexing and slicing. You can access elements by their position in the list.
Sets: Do not support indexing or slicing. Elements cannot be accessed by position.
Here's a brief example illustrating some of these differences:
# Lists
my_list = [1, 2, 3, 3, 4, 5]
print(my_list) # Output: [1, 2, 3, 3, 4, 5]
print(my_list[2]) # Output: 3
# Sets
my_set = {1, 2, 3, 3, 4, 5}
print(my_set) # Output: {1, 2, 3, 4, 5}
# print(my_set[2]) # Raises TypeError, sets do not support indexing
In the above example, the list allows duplicates and supports indexing, while the set automatically removes duplicates and does not support indexing. Choose between lists and sets based on your specific requirements for ordering, uniqueness, and mutability.
Python Coding January 07, 2024 Python Coding Challenge No comments
aList = ["Clcoding", [4, 8, 12, 16]]
print(aList[1][3])
Free Books Python Programming for Beginnershttps://t.co/uzyTwE2B9O
— Python Coding (@clcoding) September 11, 2023
Top 10 Python Data Science book
— Python Coding (@clcoding) July 9, 2023
🧵:
Top 4 free Mathematics course for Data Science ! pic.twitter.com/s5qYPLm2lY
— Python Coding (@clcoding) April 26, 2024
Web Development using Python
— Python Coding (@clcoding) December 2, 2023
🧵: