- random(): Returns a random float number between 0 and 1
- sample(): Returns a given sample of a sequence
- shuffle(): Takes a sequence and returns the sequence in a random order
- choice(): Returns a random element from the given sequence
- choices(): Returns a list with a random selection from the given sequence
- randint(): Returns a random number between the given range
- uniform(): Returns a random float number between two given parameters
Tuesday, 29 March 2022
Friday, 25 March 2022
Sequence Matcher in Python
Python Coding March 25, 2022 Python No comments
#!/usr/bin/env python
# coding: utf-8
# # Sequence Matcher in Python
# In[3]:
from difflib import SequenceMatcher
text1 = input("Enter 1st sentence : ")
text2 = input("Enter 2nd sentence : ")
sequenceScore = SequenceMatcher(None, text1, text2).ratio()
print(f"Both are {sequenceScore * 100} % similar")
#clcoding.com
# In[ ]:
Age Calculator using Python
Python Coding March 25, 2022 Python No comments
Saturday, 19 March 2022
Image to Pencil Sketch in Python
Python Coding March 19, 2022 Python No comments
Sunday, 13 March 2022
Voice Recorder in Python
Python Coding March 13, 2022 Python No comments
Download YouTube videos in Python
Python Coding March 13, 2022 Python No comments
Captcha in Python
Python Coding March 13, 2022 Python No comments
Secrets Python module
Python Coding March 13, 2022 Python No comments
Saturday, 5 March 2022
Mouse and keyboard automation using Python
Python Coding March 05, 2022 Python No comments
Friday, 4 March 2022
Python Secrets Module
Python Coding March 04, 2022 Python No comments
Monday, 28 February 2022
Digital Watch in Python using Turtle
Python Coding February 28, 2022 Python No comments
Saturday, 26 February 2022
Creating an Audiobook in Python
Python Coding February 26, 2022 Python No comments
Python module whatismyip
Python Coding February 26, 2022 Python No comments
Thursday, 17 February 2022
Collections Library in Python
Python Coding February 17, 2022 Python No comments
Saturday, 5 February 2022
Address detail through python code
Python Coding February 05, 2022 Python No comments
Track phone number using python
Python Coding February 05, 2022 Python No comments
Formatting Dates and Time Strings in Python
Python Coding February 05, 2022 Python No comments
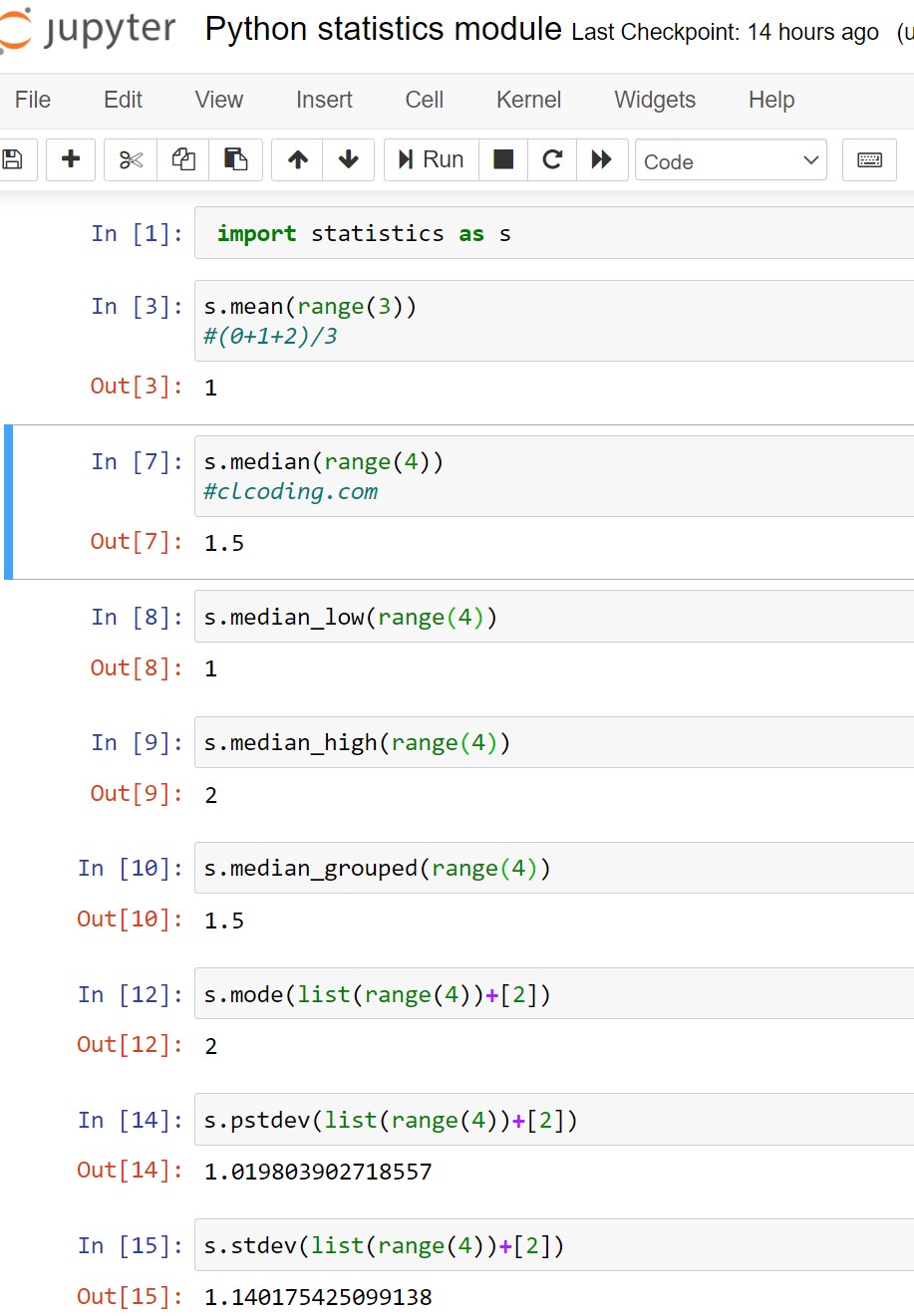
Python statistics module
Python Coding February 05, 2022 Python No comments
Saturday, 8 January 2022
Popular Python libraries used in Data Science
Author January 08, 2022 Python No comments
Scientific Computing and Statistics
NumPy (Numerical Python)—Python does not have a built-in array data structure. It uses lists, which are convenient but relatively slow. NumPy provides the high-performance ndarray data structure to represent lists and matrices, and it also provides routines for processing such data structures.
SciPy (Scientific Python)—Built on NumPy, SciPy adds routines for scientific processing, such as integrals, differential equations, additional matrix processing and more. scipy.org controls SciPy and NumPy.
StatsModels—Provides support for estimations of statistical models, statistical tests and statistical data exploration.
Data Manipulation and Analysis :
Visualization :
Machine Learning, Deep Learning, and Reinforcement Learning
Natural Language Processing (NLP)
Friday, 31 December 2021
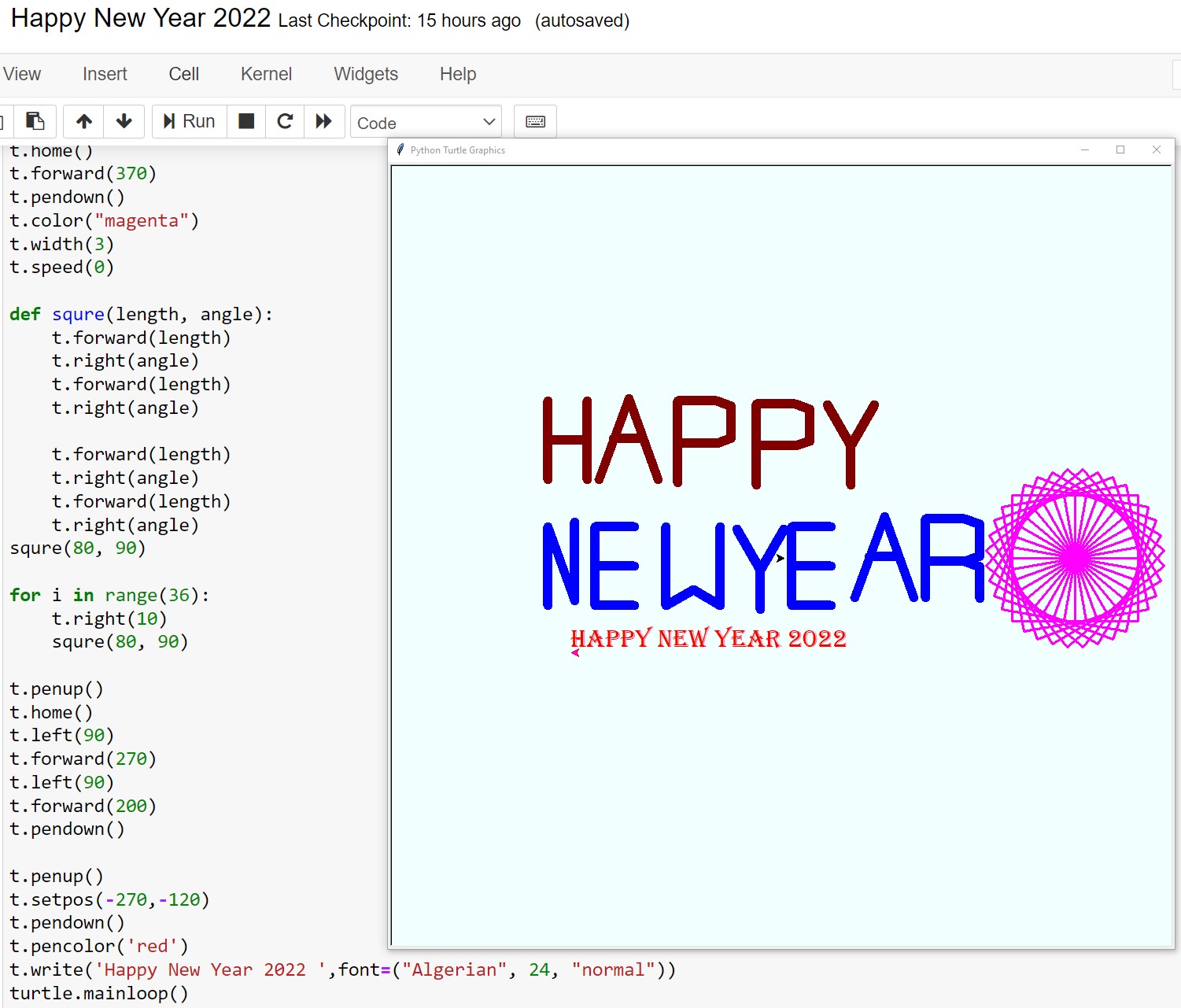
Happy New Year 2022 in Python using Turtle Library
Author December 31, 2021 Python No comments
Monday, 29 November 2021
Numpy In Python
Author November 29, 2021 Python No comments
Introduction to NumPy
Array
NumPy Array
Creation of array
Some Operations on Numpy array
Saturday, 27 November 2021
Sequence Data Part 5 | Day 9 | General Sequence Data Methods | Part I
Author November 27, 2021 Python No comments
General Sequence Data Methods | Part I
Some of the methods that we can apply on any sequential data.
So basically Python methods are like a Python function, but it must be called on an object.
And Python also has a set of built in methods that you can use on sequential data, but note that the method is going to written new values, but they are not going to change the original data at all. So we are going to look at few examples on how we can call the methods on the given sequential data.
String Methods
4) .find() - And you can also find the index of a given letter, for example, if you want to particularly know the index of a given character then you can give that inside the find method. So that should be given the single quote. So the index of n is 4.
6) .replace() - Using the method replace you will be able to replace any word with the given word. For example, you can apply or you can call that on the string and that is strsample and inside method you can just give string to be searched that is fun. So we are searching for the word fun in the strsample string and I am going to replace fun with joyful. So let me just try this. So you are getting learn is joyful. Instead of getting learn is fun which was the original string.
Friday, 26 November 2021
Java Oops Concept
Irawen November 26, 2021 Java No comments
Java Oops Concept:
1. Objects
2. Class
3. Inheritance
4. Polymorphism
5. Abstraction
6. Encapsulation
Object :
Any entity that has state and behaviour is known as an Object.
An object can be defined as an instance of a class.
Example :
Object = {property 1: value1, property 2: value 2……property n: value n}
Class :
- Collection of object is called class.
- It is a logical entity
- Class doesn’t consume any space.
- A class can also be defined as a blueprint from which you can create an individual object.
Inheritance :
When one object acquires all the properties and behaviours of a parent object, it is known as inheritance.
It provides code reusability.
It is a used to achieve runtime polymorphism.
Polymorphism :
If one task is performed in different way, it is known as polymorphism.
In java we use method overloading and method overriding.
Abstraction :
Hinding internal details and showing functionality is known as abstraction.
Encapsulation :
Binding or wrapping code and data together into a single unit are known as encapsulation.
Naming Convention :
1. Class
. It should start with the uppercase letter.
It should be a noun such as Color, Button, System, Thread, etc.
Use appropriate words, instead of acronyms.
Example :
Public class Employee {
//code snippet
}
2. Interface
It should start with the uppercase letter.
It should be an adjective such as Runnable, Remote, ActionListener.
Use appropriate words, instead of acronyms.
Example :
Interface Printable
{
//code snippet
}
3. Method
It should start with lowercase letter.
It should be a verb such as main(), print(),
println().
If the name contains multiple words, start it
with a lowercase letter followed by an uppercase letter such as
actionPerformed().
Example :
Class Employee
{
//method
Void get( )
{
//code snippet
}
}
4. Variables
It should start with a lowercase letter such as id, name.
It should not start with the special characters like & (ampersand), $ (dollar), _ (underscore).
If the name contains multiple words, start it with the lowercase letter followed by an uppercase letter such as firstName, lastName.
Avoid using one-character variables such as x, y, z.
Example :
Class Employee
{
// variables
Int id;
Char name;
}
5. Package
It should be a lowercase letter such as java, lang.
If the name contains multiple words, it should
be separated by dots (.) such as java.util, java.lang.
Example :
Package com.abc.xyz;
Class employee
{
//code
}
6. Constant
It should be in uppercase letters such as RED, YELLOW.
If the name contains multiple words, it should be separated by an underscore(_) such as MAX_PRIORITY.
It may contain digits but not as the first letter.
Example :
Class Employee
{
//constant
Static final int MIN_Age = 18;
//code
}
Object and class Example:
Public class Student {
Int id ;
String name;
Public static void main (String[] args)
{
Student s1 = new Student();
System.out.println(s1.id);
System.out.println(s1.name);
}
}
Syntax of class :
Class <class_name>{
Field;
Method;
}
Class Student {
Int rollno;
String name;
Void insertRecord(int r, String n)
{
Rollno = r;
Name = n;
}
Void display()
{
System.out.println(rollno+ “ “ +name);
}
Class StudentTest {
Public static void main (String[] args)
{
Student s1 = new student();
Student s2 = new Student();
S1.insertRecord(101, “Ram”);
S2.insertRecord(102, “Sita”);
S1.display();
S2.display();
}
}
Class Student {
Int id;
String name;
}
Class StudentTest {
Public static void main (String arg[])
{
Student s1 = new Student();
Student s2 = new student();
S1.id = 101;
S1.name = “Ram”;
S2.id = 102;
S2.name = “Sita”;
System.out.println(s1.id+ “ “ s1.name);
System.out.println(s2.id+ “ “ s2.name);
}
}
Popular Posts
-
Exploring Python Web Scraping with Coursera’s Guided Project In today’s digital era, data has become a crucial asset. From market trends t...
-
What does the following Python code do? arr = [10, 20, 30, 40, 50] result = arr[1:4] print(result) [10, 20, 30] [20, 30, 40] [20, 30, 40, ...
-
Explanation: Tuple t Creation : t is a tuple with three elements: 1 → an integer [2, 3] → a mutable list 4 → another integer So, t looks ...
-
What will the following code output? a = [1, 2, 3] b = a[:] a[1] = 5 print(a, b) [1, 5, 3] [1, 5, 3] [1, 2, 3] [1, 2, 3] [1, 5, 3] [1, 2, ...
-
What will the following Python code output? What will the following Python code output? arr = [1, 3, 5, 7, 9] res = arr[::-1][::2] print(re...
-
Through a recent series of breakthroughs, deep learning has boosted the entire field of machine learning. Now, even programmers who know c...
-
What will the following code output? import pandas as pd data = {'Name': ['Alice', 'Bob'], 'Age': [25, 3...
-
What will the output of the following code be? def puzzle(): a, b, *c, d = (10, 20, 30, 40, 50) return a, b, c, d print(puzzle()) ...
-
Step-by-Step Explanation: Dictionary Creation: my_dict = {'a': 1, 'b': 2, 'c': 3} A dictionary named my_dict is crea...
-
What will be the output of the following code? import numpy as np arr = np.array([1, 2, 3, 4]) result = arr * arr[::-1] print(result) [1, ...









































.png)






















.png)







